Geography 280b
Lecture #4
Thursday, February 3, 2000
Basic Measurement and Basic Operations II
Reading Corner
- Chapter 2: Should be read by now
Reading Assignment for next week:
- Chapter 3: “Maps as Numbers”
- (Note: slightly ahead of the outline, to take pressure off of slack week...)
The Structure of Today’s Lecture:
- Basic Measurement
- Announcements
- Basic Operations II
Basic Measurement
- Basic distance measurement —
- Measuring single straight distances.
An operation for measuring a set of distances
What it does:
- Measures distances from designated cells
Spread and its modifiers
- Euclidean version (simple spreading)
Syntax:
- DistanceSurface = Spread map to maximum distance;
Explanation of the operation and its modifiers
- This operation generates a map of spatial distances from target (non-VOID) cells in the operand map to the maximum distance or cost specified by the to modifier.
The units and the precision are specified in maximum distance
- (eg. 30km, 30.km, 30.00km are all different)
Spread is commonly known as a buffering operation
- Buffers from linear features are sometimes termed corridors.
Distance is arguably the most basic among spatial relations
- Spread explicitly measures space. It is a fundamentally spatial function.
- Almost all examples of what a GIS does use a buffers example—ad nauseum.
An Example (from Simple Computer Imaging and Mapping):
- Measuring distances from a road.
Other Examples
Using Spread to isolate the perimeter of lakes:
- Do we want the water or the beach?
There are several ways to view the results of Spread
A spreading nucleus ‘centered’ view
- Distances increase from the nuclear spreading cells outward.
- How far is X from the nucleus?
A question regarding a multi-cell ‘clot’:
- Rob's Question:
- What happens when the spreading cell is encased by other spreading cells?
- Spread always measures distances from the nearest cell.
A view from the ‘periphery’ at a target cell
- The distance from a non-nuclear point on the measured plane toward a target.
- The view from the other cells.
In which of the 2 ways does the algorithm work?
A third view: “as the helicopter flies”
A fourth view: the underlying structure — the Distance Surface
- The DistanceScape and its pits, basin slopes and ridge lines
- Question: When do we get hill/mountain slopes and peaks?
- Using image processing it is possible to show the DistanceScape as a shaded (distance) relief image. (Figure)
Ridge lines delineate Thiessen Polygons
Are Thiesen Polygons (aka Voronoi Diagrams ) doable in raster as well as in vector,
- and does that capability exist in MFworks?
Note that buffers are often portrayed by applying a Recode of every nth distance to the result of Spread
- This in effect results in contour-like distance isolines.
Spread is described as a wave of distance measurements that propagate outward from a spreading cell
- what happens to the distances between spreading cells when there are many spreading cells, bearng in mind that the computation is NOT parallel?
Spreading takes time
- There are a lot of distances to be measured.
- The spread algorithm calls for backtracking.
- Iterations compound the amount of computation.
Even so, the euclidean spread is relatively fast compared to its cousin—the non-linear Travel Cost (“Friction”) Spread
- At this point we are only introducing the Euclidean version of Spread.
- This spread operation is performed by a fast algorithm module.
- The simple spread is performed far more frequently than its fancy relative.
Non-linear distances, topographic distances, and network spreading will be described under the Rarely Used Operations category.
- They are implemented by the travel-cost spread module.
Announcements
- Assignment 3 is here
- Work on it asap, e.g. starting next week
- by ‘killing’ Assignment 2 quickly, or
- in parallel with Assignment 2
The first Ombusperson Meeting will be held next week
GIS 2000
- Questions on this?
- One day early student registration is $ 50.-
- State your day: Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday
- “Calling all Registration Forms”
- for those wishing to attend
- There will be a lecture that week
Basic Operations II
- Arithmetic
- Basic Logic
- Set Overlay (logical map overlay)
- AND, OR, NOT
- Cross
- Combine
- More on Layer Superimposition
Basic Operations II
- Basic Operations on n layers
Overlay Arithmetic
What these Operators and Functions do:
- Arithmetic expressions are commonly applied to cells on 1 or more layers.
Between cells stacked on different layers.
- For example, calculating the Standard Deviation of 40 annual Rainfall layers.
Between 1 layer and a constant.
- Example: determining whether/where a maxima condition is met.
Note that the implementation is not as individual operations.
Rather, in MF works
- these functions are implemented under the Operators and Function menus of the Script window.
- Question: What’s the reason for this ‘preferential’ treatment?
The Answer:
- Mainly because of the mathematical nature of these functions.
- It is possible to use these functions in an Algebraic Statement.
There are common conventions for building
The MFworks documentation describes the:
- Syntax
- Operators
- Functions
- Order of operations
- Mixed mode arithmetic
- VOID data
On-line documentation may help use these core ‘map algebra’ features
Basic Logic
*** Logic and its implementation in MFworks may well be on the test(s) ***
The vocabulary of logic
- the Propositional Calculus
- object term A , B
- Binary World: True or False
- Connectives
In our case object “A” really means:
- the Value Z of Cell [X,Y] on Map Layer A
- and since many or all the cells are examined, we are really referring to a two-tiered (hierarchical) compound array variable object
Connectives — the base set
| AND |
^ |
(conjunction) |
| OR |
v |
(disjunction) |
| NOT |
~ |
(negation) |
additional connectives
- IMP —>
- A—> B
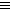 ~ (A ^ ~B)
~ (A ^ ~B) 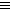 ~A v B
~A v B
- EQUIV
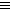
- (A —>B) ^ (B—>A)
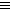 (A ^ B) v (~A ^ ~ B)
(A ^ B) v (~A ^ ~ B)
other connectives
The Truth Table for
- A^B
- AvB
- A—>B
- A
 B
B
Let’s solve together:
To be continued next week...