The dl1100 Series of Adenovirus 5 E1A Mutants
A series of small inframe deletion mutants of Adenovirus E1A was constructed in the laboratory of Dr. Stanley T. Bayley at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario Canada during the late 1980s and early 1990s.
These mutants were originally designated as the dl1100 series. They collectively delete virtually the entire E1A protein.
These mutants have been used by many laboratories throughout the world for studies of E1A function and as tools to study mechanisms regulating numerous cellular functions.
The image below describes the basic series of mutants and the region of the E1A protein deleted.
In many publications, they have been referred to by their corresponding deletions. For example, dl1102 is often referred to as delta26-35.
These mutants were originally constructed in a genomic clone of E1A (expressing 13S and 12S encoded products), but have subsequently been shifted into a 12S only background (dl520).
For example, dl1101 described the mutant in the original genomic E1A background, and dl1101/520 described the mutant in a background only expressing the 12S product.
Many of these deletions are available in combinations, which have been denoted as in the following example: dl1101 combined with dl1107 in the 12S background is dl01/07/520.
The biological effects of these mutations are listed in the Database of Ad5 E1A Mutations.
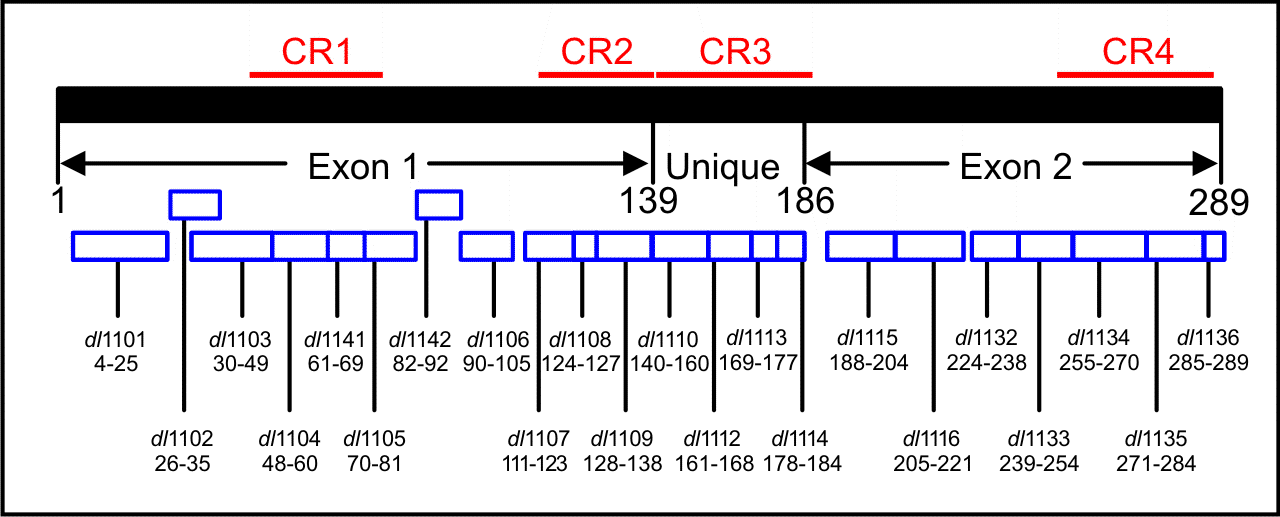
Above: Figure depicting the basic collection of Adenovirus 5 E1A mutants developed in the Bayley laboratory.
The amino acid residues deleted in each of the mutants is denoted below its name.
Initial References
Some of the origninal publications describing the construction and initial characterization of these deletion mutants are listed below.
- Use of deletion and point mutants spanning the coding region of the adenovirus 5 E1A gene to define a domain that is essential for transcriptional activation.
- Jelsma TN, Howe JA, Evelegh CM, Cunniff NF, Skiadopoulos MH, Floroff MR, Denman JE, Bayley ST.
- Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):494-502.
- PMID: 2965449
- Mapping of cellular protein-binding sites on the products of early-region 1A of human adenovirus type 5.
- Egan C, Jelsma TN, Howe JA, Bayley ST, Ferguson B, Branton PE.
- Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3955-9.
- PMID: 2975755
- Sequences in E1A proteins of human adenovirus 5 required for cell transformation, repression of a transcriptional enhancer, and induction of proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
- Jelsma TN, Howe JA, Mymryk JS, Evelegh CM, Cunniff NF, Bayley ST.
- Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):120-30.
- PMID: 2568030
- Retinoblastoma growth suppressor and a 300-kDa protein appear to regulate cellular DNA synthesis.
- Howe JA, Mymryk JS, Egan C, Branton PE, Bayley ST.
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5883-7.
- PMID: 2143024
- Ability of adenovirus 5 E1A proteins to suppress differentiation of BC3H1 myoblasts correlates with their binding to a 300 kDa cellular protein.
- Mymryk JS, Lee RW, Bayley ST.
- Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1107-15.
- PMID: 1421568
- Effects of Ad5 E1A mutant viruses on the cell cycle in relation to the binding of cellular proteins including the retinoblastoma protein and cyclin A.
- Howe JA, Bayley ST.
- Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):15-24.
- PMID: 1530776
- Induction of gene expression by exon 2 of the major E1A proteins of adenovirus type 5.
- Mymryk JS, Bayley ST.
- J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):6922-8.
- PMID: 8230413
- A region in the C-terminus of adenovirus 2/5 E1a protein is required for association with a cellular phosphoprotein and important for the negative modulation of T24-ras mediated transformation, tumorigenesis and metastasis.
- Boyd JM, Subramanian T, Schaeper U, La Regina M, Bayley S, Chinnadurai G.
- EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):469-78.
- PMID: 8440238
- Induction of apoptosis by adenovirus type 5 E1A in rat cells requires a proliferation block.
- Mymryk JS, Shire K, Bayley ST.
- Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1187-93.
- PMID: 8134121
The People that Did the Work
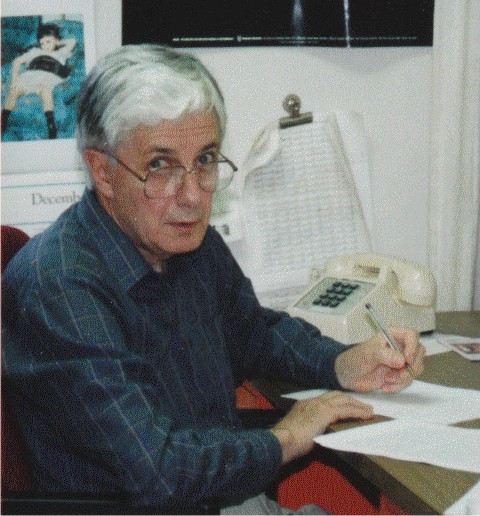 Dr. Stanley T. Bayley
Dr. Stanley T. Bayley
The mastermind of the operation.
circa 1990.
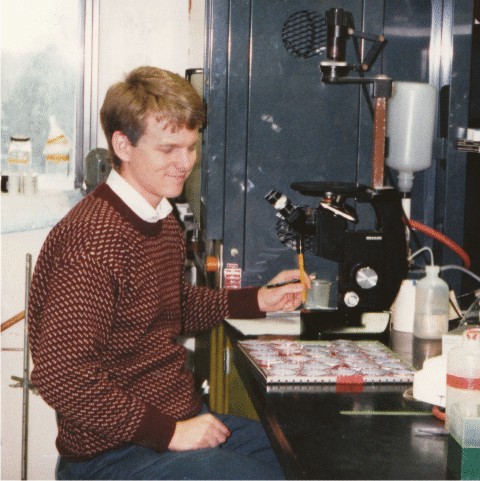 Tony Jeslsma
Tony Jeslsma
circa 1990.
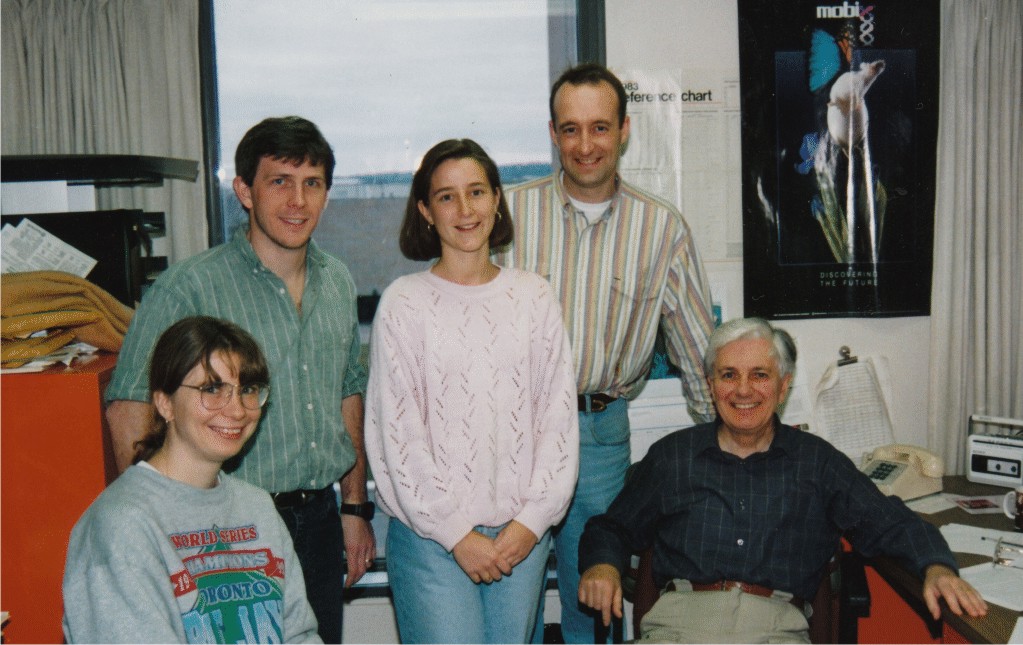 The Bayley Laboratory Members, circa 1992
The Bayley Laboratory Members, circa 1992
Kathy Shire, Joe Mymryk, Susan Shepherd, John Howe and Stan Bayley
(from left to right)
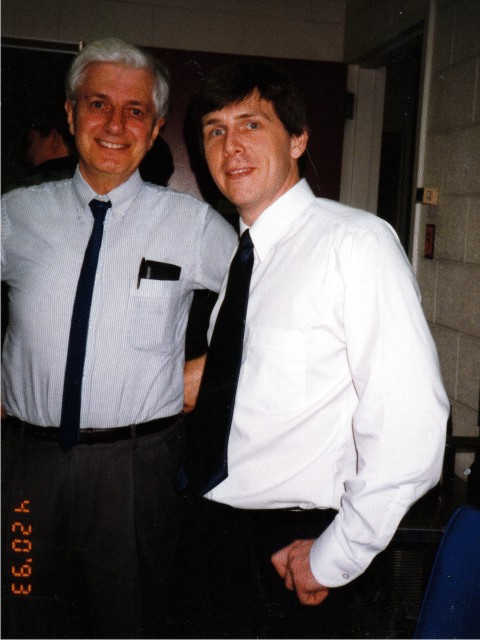 Stan Bayley and Joe Mymryk
Stan Bayley and Joe Mymryk
Stan Bayley and I after my Ph.D.thesis exam in 1993.
go back to main page


 Dr. Stanley T. Bayley
Dr. Stanley T. Bayley Tony Jeslsma
Tony Jeslsma The Bayley Laboratory Members, circa 1992
The Bayley Laboratory Members, circa 1992 Stan Bayley and Joe Mymryk
Stan Bayley and Joe Mymryk